What Is a Test Automation Strategy?
A test automation strategy is a structured plan that defines what to automate, how to automate it, which tools to use, and how automated tests integrate into the development lifecycle. A strong strategy helps teams scale testing, reduce manual effort, and maintain software quality as delivery speed increases.
Key Takeaways
- A test automation strategy defines scope, tools, frameworks, and integration with CI/CD.
- Not all tests should be automated; focus on high-impact, repeatable scenarios.
- A scalable framework and stable environments are critical for long-term success.
- Continuous monitoring and iteration keep automation reliable and valuable.
- Most teams succeed with a phased, hybrid approach to automation.

As software teams grow and ship faster, a thoughtful software test automation strategy becomes the difference between smooth releases and late-night bug hunts.
A test automation strategy gives your team a shared direction and the confidence to move quickly while maintaining high-quality standards. When done well, automation reduces manual effort, boosts coverage, and speeds up feedback, making releases more predictable and giving your team time to focus where it counts.
Without a clear strategy, however, automation can become inefficient and unsustainable. Teams may invest in the wrong areas, struggle with fragile test suites, or face misalignment in their toolchain. Over time, this slows progress and introduces risk, often when it’s least welcome.
In this guide, we’ll cover how to create an effective strategy, from setting goals to choosing tools and continuously improving, so your team can scale quality with confidence.
A Simple Test Automation Strategy Framework (5 Core Pillars)
An effective test automation strategy typically includes five core pillars:
1. Clear automation goals tied to business outcomes
2. Defined scope across test levels (unit, integration, end-to-end)
3. A scalable automation framework and toolchain
4. CI/CD integration for continuous feedback
5. Ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and improvement
These pillars ensure automation remains reliable, maintainable, and aligned with delivery speed.
The rest of this guide walks through each of these pillars in detail, starting with defining clear automation goals and scope.
1. Defining Goals and Scope for Your Test Automation Strategy
Before writing a single line of automated test code, take a moment to pause and align. A successful automation strategy starts with clear, measurable goals and a well-defined scope. Ask your team: What are we trying to achieve with automation—and why now?
Your automation efforts should map directly to business outcomes. If you're aiming to shorten release cycles, prioritize regression tests that ensure deployment stability. If the focus is on reliability in a mission-critical flow, start with end-to-end coverage for that journey. Whether your goal is speed, risk reduction, better coverage, or fewer production bugs, make that purpose your north star.
Need to define your overall testing approach before diving into automation? Here’s a practical guide to building a full test strategy.
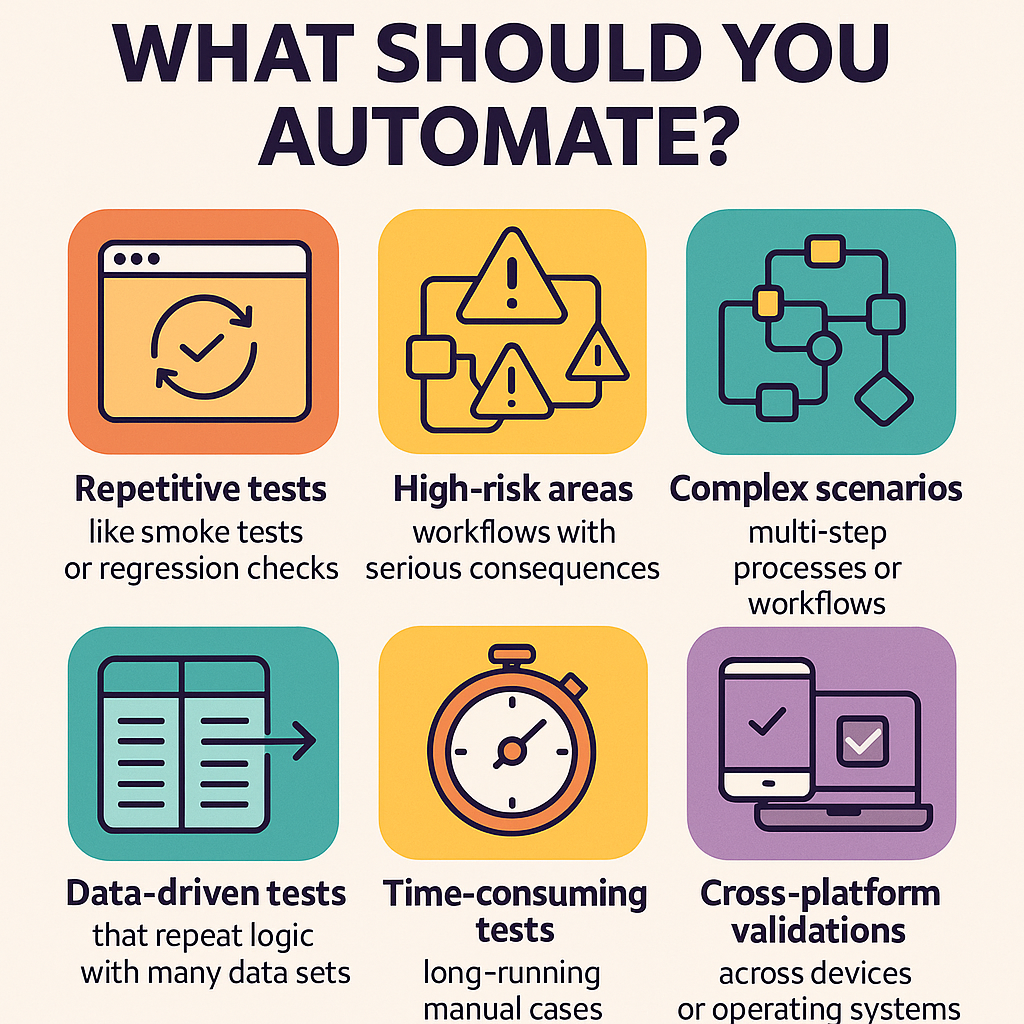
What Should You Automate?
Not every test needs to be automated. In fact, trying to automate everything can lead to wasted time and brittle test suites. Focus on areas where automation delivers the highest impact:
-
Repetitive tests – like smoke tests or regression checks that run often and change infrequently.
-
High-risk areas – workflows where a failure would have serious consequences (e.g., payments or login flows).
-
Complex scenarios – multi-step processes or workflows with heavy data input.
-
Data-driven tests – scenarios that repeat the same logic with many data sets.
-
Time-consuming tests – long-running manual cases that slow your team down.
-
Cross-platform validations – tests that must run across different devices, browsers, or operating systems.
These are great places to start because they reduce manual burden while increasing consistency and test confidence.
Understand the Levels of Testing
Automation applies differently across the various layers of your application. Make sure your scope includes a healthy mix:
-
Unit tests check individual components in isolation. They're fast, cheap, and perfect for automation.
-
Integration tests validate how modules or services work together.
-
System (end-to-end) tests simulate real-world workflows from start to finish.
-
Acceptance tests confirm that the application meets business or user requirements.
Each level serves a different purpose. Together, they form a strong testing strategy.
The testing pyramid is a helpful guide: focus most of your automation at the unit test level, build a solid layer of integration tests, and be selective about end-to-end tests. This structure keeps your suite fast, maintainable, and comprehensive.
Set Clear, Trackable Objectives
Good strategies are measurable. Define what success looks like. Perhaps it's reducing regression testing time from two weeks to two days, or achieving 80% automation coverage on critical user flows. Clear objectives help track progress and drive accountability.
Just as importantly, involve your whole team. Product managers, developers, QA—all stakeholders should weigh in on what to automate and what to leave manual. When everyone’s aligned, your automation strategy becomes a shared investment in quality.
2. Selecting the Right Automation Testing Tools and Frameworks
Once you've defined what to automate, the next step is selecting the right automation testing tools to support your strategy. These choices will directly impact how scalable, maintainable, and efficient your test automation efforts become.
When evaluating tools, prioritize:
-
Compatibility with your tech stack and target platforms (web, mobile, API, desktop).
-
Ease of use and alignment with your team’s skills.
-
CI/CD integration, so tests run automatically as part of your development workflow.
-
Scalability, reporting, and long-term maintainability.
To help you make an informed decision, we’ve put together a detailed breakdown of the most widely used automation tools in the industry, both open-source and commercial:
This guide covers tools such as Selenium, Cypress, Appium, and more, helping you compare features, use cases, and integration options.
Keep in mind: most teams don’t rely on a single tool. A typical automation toolchain may include unit testing libraries (such as JUnit or pytest), UI testing tools (like Selenium or Playwright), API testing tools (like Postman or Rest Assured), and test management platforms like TestRail.
With the right tools in place, the next step is to design a test automation framework that provides your tests with structure and longevity.
3. Designing a Scalable Test Automation Framework
Selecting the right tools is essential, but how you organize your tests matters as much. A well-designed test automation framework is the backbone of sustainable, scalable automation. It defines how your team writes, organizes, runs, and maintains test code across your suite, helping you grow coverage efficiently while keeping things clean and collaborative.
Common Types of Test Automation Frameworks
Each framework type serves a different purpose, and many teams end up combining elements based on their needs:
-
Linear Framework: This approach is best for small projects or quick prototypes. It follows a simple "record and playback" model. It's easy to start with, but it lacks modularity and doesn’t scale well.
-
Modular Framework: This framework organizes tests into reusable components or modules (e.g., Login, and Checkout). When one module changes, updates cascade automatically, making it ideal for larger, evolving applications.
-
Data-Driven Framework: This style separates test logic from test data. You can run the same test with different input values using data files like CSV or JSON, which saves time when testing multiple conditions or user types.
-
Keyword-Driven Framework: This framework uses high-level keywords (like “Click Button” or “Verify Text”) instead of code. It is great for collaboration between technical and non-technical team members and is often used with spreadsheet-based test cases.
-
BDD Framework (Behavior-Driven Development): Tools like Cucumber or SpecFlow allow you to write tests using Given/When/Then syntax in plain English. These frameworks bridge the gap between product, QA, and dev teams by turning scenarios into living documentation.
-
Hybrid Framework: Most real-world frameworks combine elements of the above. For example, you might have modular test components, run them with different datasets, and wrap them in BDD-style syntax. Flexibility is key.
For a deeper dive into these framework types, check out our guide to automation testing frameworks.
Best Practices for Designing Your Framework
No matter which structure you choose, these principles will help keep your test suite reliable and maintainable:
-
Follow coding conventions: Establish naming standards and folder structures to ensure consistency across your test suite.
-
Keep tests independent: Every test should run in isolation. Avoid dependencies between tests to support parallel execution and faster debugging.
-
DRY (Don’t Repeat Yourself): Reuse common test logic via helper functions or shared modules. This reduces duplication and simplifies updates.
-
Use the Page Object Model (POM): Especially useful in UI automation, POM organizes your test code by representing each page or component as an object. It improves clarity and makes your tests resilient to UI changes.
-
Support multiple environments: Include config files or environment variables to easily run your tests across development, staging, or production environments without code changes.
-
Built-in logging and reporting: To speed up debugging and track test outcomes, capture detailed logs, screenshots of failures, and structured test reports (like JUnit XML).
-
Version control your test code: Like application code, test scripts should be stored in Git or your preferred version control system (VCS). This makes collaboration easier and keeps a history of changes.
-
Ensure CI/CD compatibility: Your framework should integrate smoothly into your CI/CD pipeline. That means tests must be executable from the command line and produce outputs your pipeline can read.
Designing a great automation framework takes upfront effort but pays off in faster feedback, lower maintenance, and a testing process that grows with your product. With a strong foundation, your team can scale automation confidently and sustainably.
4. How to Implement a Test Automation Strategy
With your test automation strategy defined and your framework in place, it’s time to bring it all to life. This phase is where plans become action, as you set up your test environments, write and manage your automated test scripts, and embed tests into your CI/CD pipeline for continuous feedback.
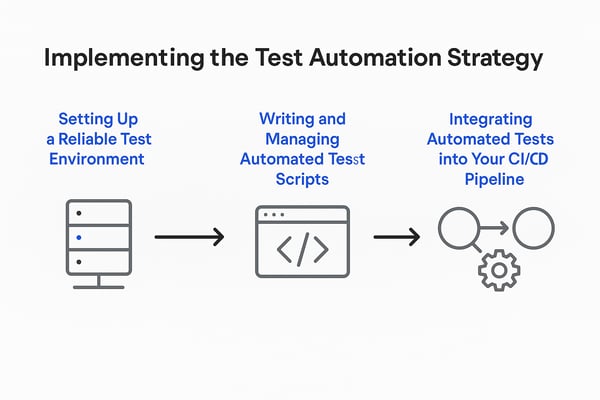
1. Setting Up a Reliable Test Environment
A successful automation rollout starts with a stable and realistic test environment. Your environment should mirror production as closely as possible, including databases, services, configurations, and any prerequisites (such as SSL certificates, user accounts, and feature flags). This reduces false failures and gives your team confidence that passing tests reflects production reality.
You have a few options:
-
Dedicated QA environments for continuous testing
-
Ephemeral environments spun up with containers or cloud tools for clean, isolated runs
-
Production-like environments for smoke or sanity checks post-deployment
Managing test data is just as important. Consider:
-
Creating controlled datasets for repeatable results
-
Using setup scripts or APIs to generate the needed test data
-
Resetting the environment state before runs (via snapshots, Docker images, etc.)
Also, ensure that the environment setup steps are well documented. Anyone on your team should be able to spin up a test-ready environment quickly and reliably.
2. Writing and Managing Automated Test Scripts
Once your environment is stable, focus on building reliable and maintainable test cases. Start with high-priority scenarios, such as core workflows, business-critical paths, and high-risk areas identified in your automation scope.
Best practices for writing effective test scripts:
-
Stick to your framework design: Use page objects, test modules, or data-driven patterns as planned.
-
Write clear, focused tests: Each script should validate one core scenario to simplify debugging.
-
Use strong assertions: Validate outputs, UI changes, data updates, and any side effects to ensure accuracy.
-
Handle setup/teardown logic: Use
@Before/@After(or equivalent) to prepare the test state and clean up afterward. -
Track test data versions: Keep test data (like CSVs or fixtures) in version control alongside the tests.
-
Document edge cases: Leave helpful comments for anything unusual—timing workarounds, known flakiness, or test dependencies.
Build your suite incrementally. Start small, validate early scripts locally, and expand as you gain confidence. Running tests frequently during creation helps surface framework or environment gaps before they become blockers.
3. Integrating Automated Tests into Your CI/CD Pipeline
This is where automation delivers its full value by continuously validating your code in real time.
There are several levels of CI/CD testing integration:
-
CI test runs on code commits: Trigger fast tests (unit, smoke, API) on every push or pull request using tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, CircleCI, or GitHub Actions. This provides rapid feedback and prevents broken code from being merged.
-
Scheduled test executions: Run longer suites (like regression tests) nightly or weekly. This ensures full coverage without slowing down your dev cycle.
-
Post-deployment tests: Automatically validate deployments with sanity checks in staging or even production (using read-only tests). This adds confidence after releases go live.
To support this, configure your CI pipeline to:
-
Run tests from the command line or scripts
-
Generate reports (e.g., JUnit XML) for easy parsing
-
Publish results in dashboards or notifications (email, Slack, etc.)
-
Fail builds on critical test failures to enforce quality gates
-
Handle environment provisioning and teardown (e.g., spin up containers, reset DBs, clean services)
Define test tiers: must-pass tests (e.g., login, checkout) should block releases, while optional tests (e.g., UI layout verifications) can alert without halting deployment. This gives teams control without friction.
4. Closing the Feedback Loop
When implemented effectively, automation becomes part of your team’s natural rhythm. Developers push code and get meaningful feedback within minutes. This continuous testing loop enables faster releases, tighter quality control, and fewer surprises late in the cycle.
By the end of implementation, you should have:
-
Reliable environments with repeatable test data
-
A growing suite of automated test scripts
-
Smooth CI/CD integration for continuous feedback
It’s the foundation for scaling automation and your team’s ability to move faster without sacrificing quality.
5. Measuring and Improving Your Test Automation Strategy
Getting your automated testing up and running is a significant achievement, but it’s not the finish line. A successful test automation strategy is not a one-time effort; it’s a living, evolving system that needs regular monitoring, reporting, and iteration to remain valuable and reliable.
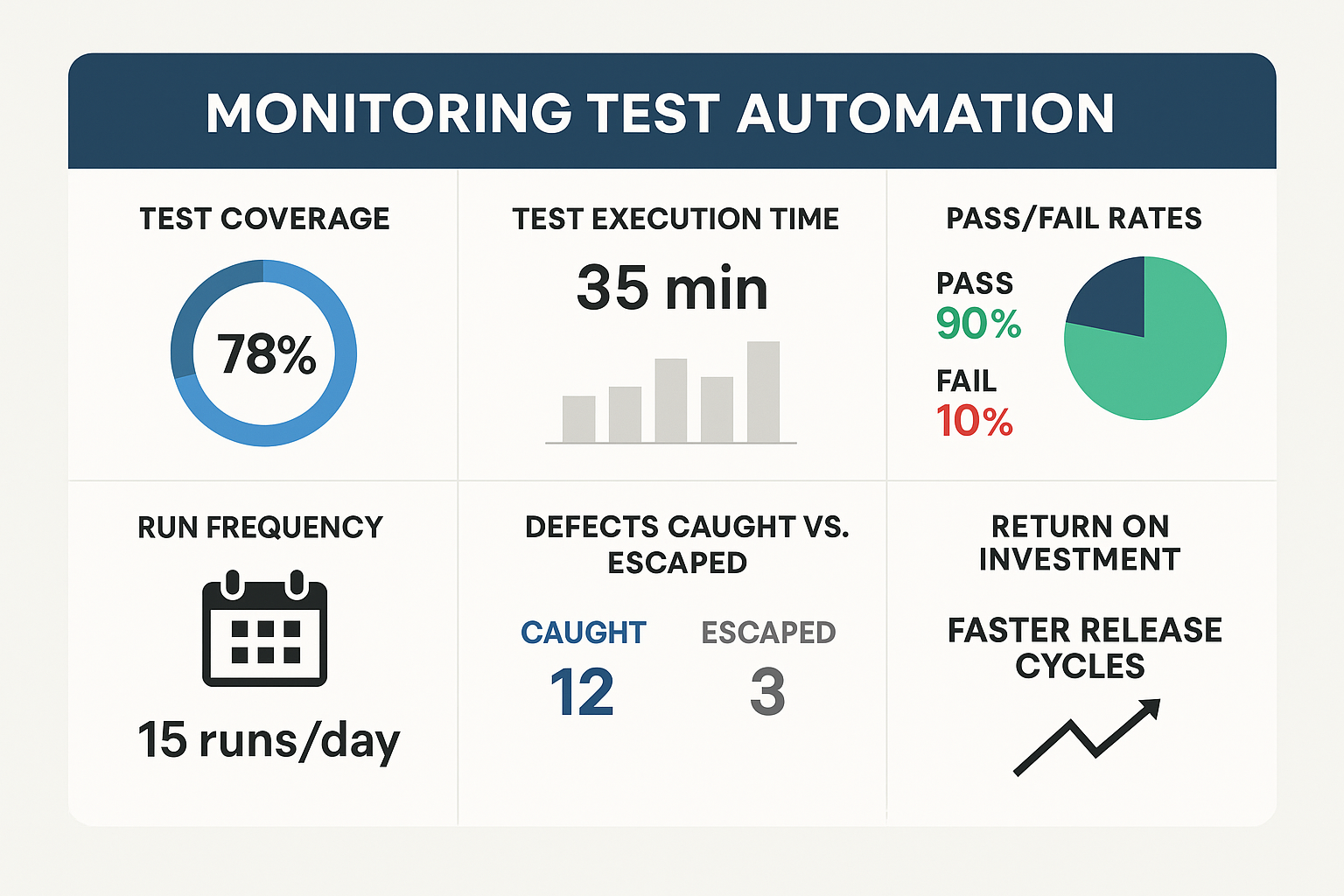
1. Monitoring Test Automation with Metrics and Dashboards
Once your automated tests are in motion, tracking their performance is essential. The right metrics provide both real-time visibility and long-term insights into how well your strategy is working.
Here are the key test automation metrics to monitor:
-
Test Coverage
Measure how much of your application is covered by tests. This includes:-
Code coverage (lines or branches executed)
-
Requirements coverage (user stories or features with associated tests)
While 100% is rarely necessary, higher coverage in critical areas builds confidence and reduces risk.
-
-
Test Execution Time
Track how long it takes to run your full test suite. Rising execution times can signal inefficiencies or indicate the need to split tests for parallel execution, especially in continuous integration (CI) pipelines. -
Pass/Fail Rates and Flakiness
Monitor stability across builds. Consistent failures typically indicate product or test issues, while inconsistent results often indicate flaky tests that require cleanup. A healthy suite should be predictably green. -
Run Frequency
Evaluate how often your suite runs:-
On every code change for rapid feedback (CI)
-
Nightly or pre-release for complete regression. Regular execution is the best defense against regressions.
-
-
Defects Caught vs. Escaped
Track the number of issues caught by automation before release versus those found in production. The goal is to shift detection as far left as possible. -
ROI from Automation
Estimate return by comparing testing cycle time, manual effort saved, and release cadence improvements. Fewer bugs, shorter test cycles, and faster releases are all signs that automation is paying off.
Use automated testing dashboards to visualize these metrics. Most CI tools (like GitLab, Jenkins, or CircleCI) offer built-in reporting, and test management tools can provide structured dashboards and trend analysis.
2. Tailoring Test Reporting for Different Stakeholders
Not everyone needs the same level of detail. Customize your test reporting strategy to ensure the right insights reach the right people:
-
For Developers & QA Engineers:
Provide detailed test reports with error messages, logs, and stack traces. CI tools usually generate these automatically. Integrate real-time alerts (via Slack or email) to surface failures. -
For QA Managers & PMs:
Deliver high-level overviews—pass/fail summaries, test coverage stats, and trend charts. Dashboards help assess release readiness and resource needs. -
For Business Stakeholders:
Translate results into impact. For example: “Our average release cycle dropped from 3 weeks to 10 days since implementing CI-integrated test automation.”
Highlight success stories, cost savings, and risk reductions. Charts and visual summaries make your impact tangible.
Dashboards, alerts, and integrations with chat tools or wallboards help ensure test visibility. A green build should feel like progress, while a red one should prompt team attention.
3. Continuous Improvement: Evolve with Purpose
The best test automation strategies aren’t static; they grow with your product, team, and users. Build in space for reflection and refinement.
Key practices to embed continuous improvement in test automation:
-
Regular Suite Reviews
Schedule time (e.g., every sprint or month) to clean up flaky tests, remove outdated cases, and update scripts to reflect recent product changes. -
Root Cause Analysis for Failures
Don’t just rerun failed tests; investigate why they failed. Was it a product bug, an environment issue, or a brittle test? Learn from it and improve. -
Adapt to Product & Tech Changes
If your team adds new platforms (e.g., mobile apps), expand your automation to cover them. Tools like Appium can help. Keep your strategy in sync with your roadmap. -
Stay Current with Tools & Trends
Explore new tools or services periodically. Innovation in automation is constant, from cloud-based test grids to AI-driven test maintenance. Test small before adopting at scale. -
Listen to Your Team
Use retrospectives and 1:1s to gather feedback. Are tests fast enough? Are the results clear? Are tools slowing anyone down? Automation is a team effort; refining it should be too. -
Audit & Evolve Test Cases
Remove tests for deprecated features. Add new ones for recent bugs or user flows. Keep your suite lean, relevant, and high-value.
At its core, automation exists to build trust in your code, your team, and your release process. If the suite becomes noisy, brittle, or hard to use, that trust erodes. Monitor closely, iterate often, and treat your test suite like a product that requires care, investment, and collaboration to thrive.
If done right, your automation will not only keep pace with your development but also help drive it forward.
Common Test Automation Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with a solid test automation strategy, challenges will arise. Success depends not on avoiding them, but on how effectively you identify and resolve them. Below are three of the most common automation hurdles and how to confidently overcome them.
1. Flaky Tests That Undermine Trust
Flaky tests that pass or fail inconsistently without code changes can quickly erode confidence in your test suite. Timing issues, concurrency conflicts, or external dependencies often cause them.
How to fix flaky tests:
-
Use explicit waits or smart synchronization to ensure the application is in the correct state before actions are taken.
-
Isolate test data and ensure each test runs in a clean environment to avoid state leakage between tests.
-
Mock or stub unreliable external services when possible, especially for third-party APIs or non-deterministic systems.
-
Avoid retrying as a crutch. While limited retries in CI can filter out rare flukes, the long-term fix is resolving the root cause.
When your team trusts that a failing test really indicates a bug, you maintain the integrity of your entire automation process.
2. Team Collaboration & Skill Gaps
Test automation is a team effort, but in many organizations, it’s siloed. Developers might focus only on unit tests, while QA owns end-to-end automation. This disconnect slows progress and leads to brittle strategies.
How to build a collaborative automation culture:
-
Encourage developers to review and contribute to test code, just like they do with production code.
-
Invest in cross-training testers in scripting and developers in testing best practices.
-
Introduce BDD frameworks (like Cucumber or SpecFlow) to involve product, QA, and engineering in shared test definitions.
-
Publicly celebrate automation wins, like a critical bug caught before release, to reinforce its business value.
When quality is everyone’s job, automation becomes stronger, faster, and more sustainable.
3. Inconsistent Test Data and Environments
Inconsistent test environments and data are major sources of false negatives and wasted debugging effort. What works on one machine may fail in CI, or pass with one dataset and fail with another.
How to stabilize your test environment and data:
-
Use unique test data (e.g., appending timestamps or GUIDs) to avoid collisions.
-
Set up API or DB-based setup and teardown routines to create and clean test data dynamically.
-
Leverage Infrastructure as Code (IaC) to provision identical environments across local, QA, and CI pipelines.
-
For complex systems, use Docker, Docker Compose, or cloud test environments to isolate services.
-
Document and automate environment setup to eliminate human guesswork and avoid configuration drift.
The more predictable your environment, the more meaningful your test results.
Other Challenges in Test Automation Strategy
You may also encounter:
-
High initial setup costs
-
Tooling or integration gaps with existing systems
-
Ongoing test maintenance as features evolve
-
Difficulty measuring ROI from automation investments
These are common across teams of all sizes and maturity levels. The key is to stay proactive. Revisit your strategy often, adapt based on your team's learning, and iterate with purpose. No test automation process is perfect from the start, but continuous feedback and refinement make it truly effective over time.
When to Consider a Test Automation Partner
If these challenges feel familiar or your team is stretched too thin to build and maintain automation in-house, this may be the right time to explore a dedicated solution.
A platform like MuukTest is built to solve these exact challenges, offering intelligent, low-maintenance test automation that scales with your product. From fast onboarding to smart, AI agents and built-in reporting, MuukTest helps teams reap the benefits of automation without the operational burden.
If you want to speed up releases, reduce manual testing, and regain confidence in your automation suite, learn how MuukTest can help.
Building a Sustainable Test Automation Strategy
A strong test automation strategy doesn’t just help you catch bugs; it enables you to move faster, release with confidence, and reduce manual testing overhead.
By now, you’ve seen the key building blocks:
-
Set clear goals that tie automation to business value
-
Focus on high-impact tests to get quick wins
-
Choose tools and frameworks that your team can support
-
Integrate tests into your CI/CD pipeline
-
Monitor results and improve over time
Whether you're just getting started or optimizing an existing setup, the most important thing is to keep moving forward. Start small, learn from what works, and adapt as your product and team evolve.
And if your team is short on time or resources, tools like MuukTest can help simplify the process, offering smart, low-maintenance test automation that scales with your needs.
See how MuukTest can support your testing strategy
Quality software doesn't happen accidentally. It’s built through intention, collaboration, and the right tools. Keep your strategy simple, your tests reliable, and your team focused on what matters most.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a test automation strategy?
A test automation strategy is a structured plan that defines which tests should be automated, which tools and frameworks to use, how automation fits into the development lifecycle, and how test suites are maintained over time. A strong strategy ensures automation supports speed, reliability, and scalability as software evolves.What should be included in a test automation strategy?
An effective test automation strategy typically includes:
- Clear automation goals tied to business outcomes
- Defined scope across test levels (unit, integration, end-to-end)
- Selection of tools and frameworks aligned with the tech stack
- CI/CD integration for continuous feedback
- Metrics for monitoring coverage, stability, and ROI
- A plan for ongoing maintenance and improvement
Together, these elements help teams avoid brittle test suites and ensure long-term value from automation.
When should a team start test automation?
Teams should begin test automation when they have stable features that are tested repeatedly, such as regression or smoke tests. Starting too early can lead to high maintenance costs, while starting too late can slow releases and increase risk. Many teams begin with a small, high-impact scope and expand automation as the product matures.
What are the most common mistakes in test automation strategies?
Common mistakes include trying to automate everything, choosing tools that don’t fit the team’s skills, neglecting test maintenance, and failing to integrate automation into CI/CD pipelines. Without a clear strategy, automation can become fragile, slow, and difficult to scale.How do teams scale a test automation strategy over time?
Scaling automation requires regularly reviewing test coverage, removing flaky or low-value tests, and expanding automation into new areas as the product grows. Teams often evolve toward a hybrid approach, balancing automated tests for stability and speed with manual testing for usability and exploratory scenarios.
Some teams choose to accelerate this process by working with solutions like MuukTest, which help teams implement and maintain test automation using AI-driven tooling combined with QA expertise. This approach can reduce maintenance overhead and make it easier to scale automation without building everything in-house.
Does a test automation strategy replace manual testing?
No. A test automation strategy complements manual testing rather than replacing it. Automation is best for repetitive and high-volume tests, while manual testing remains essential for usability, exploratory testing, and validating new or rapidly changing features.