You’ve just shipped a new feature. It passed QA, looked great in staging… and then a customer finds a broken button in Safari or a misaligned layout on mobile. Worse yet, a key user flow fails in production.
These types of UI regressions are more than frustrating; they’re costly. And for engineering leaders, they reveal a bigger issue: manual UI testing can’t keep pace with the speed, complexity, and visual demands of modern software. Manually clicking through every scenario is time-consuming, error-prone, and drains valuable team capacity. It slows down releases and leaves room for inconsistencies that damage user trust.
Automated User Interface (UI) testing offers a smarter, faster alternative. By simulating real user interactions through scripts and specialized tools, it continuously validates the UI across browsers, devices, and screen sizes. It helps teams catch issues earlier, release with greater confidence, and shift QA resources toward more strategic work.
For CTOs, VPs of Engineering, and QA leaders, UI automation isn’t just a tactical improvement — it’s a strategic lever for delivering better software, faster. This guide explores how to harness it effectively, from selecting the right tools to implementing best practices, so you can scale testing without sacrificing quality.
Key Takeaways
- Automated UI testing boosts speed, quality, and confidence
It helps teams catch bugs earlier, reduce manual effort, and ship faster without sacrificing user experience. - It’s a strategic lever, not just a QA upgrade
For engineering leaders, UI automation improves ROI, scales testing efficiently, and protects the product experience at every release. - Manual and automated testing work best together
Use automation for regression and consistency, and manual testing for exploration and UX—each strengthens the other. - Success depends on the right tools, structure, and practices
Stable frameworks, clean scripts, CI/CD integration, and resilient test design are key to long-term impact.
What is Automated UI Testing?
Automated UI testing, also known as UI automation testing or automated user interface testing, uses scripts and tools to simulate real user interactions with an application’s interface. It verifies that buttons, forms, navigation, and on-screen workflows behave as expected, without requiring human testers to click through each step manually.
Think of it as a “robot user” that performs the same actions a person would: clicking buttons, entering text, selecting options, and checking results. These scripts can run anytime, after every code push, across multiple browsers, and on various devices, to catch UI issues early and often.

Key automated UI tests components and steps
- Identifying UI elements: Test scripts locate UI components, such as buttons, input fields, and links, using unique identifiers (IDs, classes, XPath, etc.) to interact with the correct elements on the page.
- Simulating user interactions: Scripts mimic how a real user would use the app – clicking buttons, entering text, selecting options, navigating through screens, and so on – to exercise the interface thoroughly.
- Verifying expected behavior: After each interaction, the test checks outcomes, ensuring that submitting a form saves data and displays a confirmation, that clicking “Add to Cart” updates the cart count, or that a modal dialog appears as expected. The script compares the actual UI state or output to the expected result.
- Handling dynamic content: Good UI tests account for things like asynchronous loads or animations. For example, the script will wait for a page element to appear or a progress spinner to disappear before trying to click the following button, preventing false failures due to timing issues.
By automating these interactions and checks, you can run a suite of UI tests at any time (e.g., on every code push or nightly), consistently covering complex user flows. This ensures your application’s interface works as intended across different scenarios and devices, all while freeing your team from repetitive manual testing cycles.
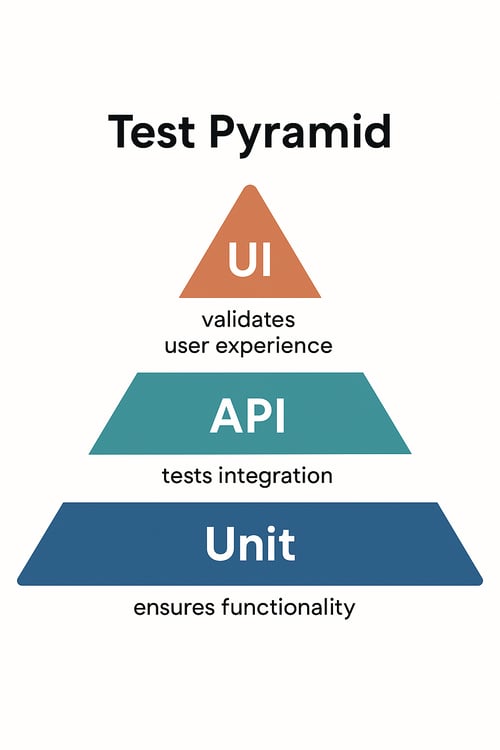
Where Automated UI Testing Fits in the Test Pyramid
UI tests are powerful, but they’re just one layer of a complete testing strategy.
In the testing pyramid model, tests are organized by scope and speed:
-
Unit tests, at the base, are fast, stable, and verify individual functions.
-
API/service-level tests check backend logic and system communication.
-
UI tests (at the top) validate the full user experience, but tend to be slower and more brittle.
That’s why UI testing should target critical user flows, while unit and API tests handle broader coverage. Used together, they create a balanced, high-confidence suite.
Manual vs. Automated UI Testing: A Strategic Comparison
Both manual and automated UI testing aim to ensure that the product works visually and functionally. However, their impacts, costs, and scalability differ.
| Aspect | Manual UI Testing | Automated UI Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slow; testers work step-by-step | Fast; runs in seconds or minutes |
| Accuracy | Susceptible to human error | Precise and repeatable |
| Scalability | Limited by team size | Can scale across thousands of tests, browsers, and devices |
| Test Coverage | Selective and shallow | Broad, deep, and repeatable |
| Maintenance Effort | Minimal, but time-intensive to repeat | Requires upkeep as UI evolves |
| Cost Over Time | Increases with every new test cycle | Drops over time after initial setup |
| Best Use Case | Exploratory and visual edge cases | Regression and core functional flows |
Manual testing still has a place, especially for exploratory and usability testing. However, automation is the only scalable path forward for repeatable regression checks and release validation.
Benefits of Automated UI Testing
Automating your UI tests can deliver significant benefits to your software development lifecycle and business outcomes. Here are some of the key advantages:

Improve Efficiency and Speed
Automated tests execute repetitive tasks much faster than human testers. This speed allows for quicker feedback cycles, accelerating your development process. Imagine running hundreds of UI test cases in minutes - something impossible with a manual approach. This rapid feedback helps identify and fix bugs early, saving your team valuable time and effort.
Moreover, automated UI testing frees up your QA engineers to focus on more exploratory and creative testing areas that truly require human insight, rather than spending hours on rote click-throughs. In other words, you’re leveraging machines to handle the monotonous checks, allowing your team to tackle higher-level quality challenges. The result is a more streamlined and Agile workflow for development and testing.
Enhance Accuracy and Reliability
Human error is inevitable in manual testing; steps can be skipped, results can be misinterpreted, or edge cases can be overlooked. Automated UI testing eliminates variability in test execution, ensuring consistent and precise results every time. Tests run exactly as they are scripted, so you won’t have false negatives or missed bugs due to tester fatigue or oversight. This leads to more reliable outcomes and gives you greater confidence in the quality of each build.
It also simplifies debugging: when an automated test fails, you know it’s due to a genuine issue (not a tester mistake), and you can reproduce that failure easily for developers. This increased accuracy and consistency ultimately contribute to a more robust and dependable software product.
Reduce Long-Term Costs and Risks
While setting up automated UI testing requires an initial investment in tools, framework development, and script writing, it yields significant long-term cost savings.
By catching defects early in the development cycle, you avoid the exponentially higher costs of fixing bugs in production or late-stage testing. Automation also shortens test cycles – what might take a team of manual testers days or weeks can often be done in hours by automated tests, meaning you can release faster (and pay less in man-hours for regression testing each cycle).
Fewer bugs escaping to production also means lower maintenance and customer support costs. For engineering leaders, these efficiencies improve the ROI of QA efforts – resources spent on testing go further, and the team can reallocate the saved time to new feature development or other priorities. This cost-effectiveness makes automated UI testing not just a QA improvement, but a wise business investment in the long run.
Increase Test Coverage and User Confidence
Automated UI testing allows you to significantly increase your test coverage across browsers, devices, and scenarios. Because tests can run quickly and in parallel, you might cover dozens of combinations (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge; desktop and mobile views; different user roles) that would be infeasible to test exhaustively by hand.
Broad coverage means you catch more edge cases and ensure a consistent user experience for all users. For example, you can automatically verify that your web app works on Chrome and Safari, or test an entire end-to-end purchase flow with every payment method – all with minimal additional effort. This comprehensive approach reduces the risk of unexpected bugs popping up in corners of the application that weren’t manually checked. Higher coverage leads to a more reliable, high-quality product and improves user satisfaction, as customers encounter fewer issues.
Many organizations that use UI automation have managed to deliver new features with zero critical UI bugs because their automated tests cover the major use cases. In short, you gain confidence that if it passes your automated suite, it will work for users in production.
Key Components for Automating UI Testing
Effective UI test automation relies on more than just writing test scripts — it requires the right combination of tools, code quality, and infrastructure to ensure speed, accuracy, and long-term maintainability.
1. The Right Automation Tool for the Job
The first step is selecting a UI automation testing tool that fits your application type and tech stack. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution — the best tool depends on what you’re testing and who’s doing the testing.
Some of the most widely used automated UI testing tools include Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, and Appium, each suited to different platforms and team needs.
Your choice should also consider:
-
Team skillsets (do your engineers know JS, Python, Java?)
-
CI/CD compatibility
-
Browser/device requirements
-
Support for parallel execution or visual regression testing
2. Well-Structured, Maintainable Test Scripts
Once you’ve chosen a tool, the next step is building high-quality test scripts. These scripts define:
-
What to interact with (buttons, input fields, navigation elements),
-
What actions to perform (clicks, text entry, scrolls),
-
What outcomes to expect (form submission, UI state change, confirmation messages)?
Effective test scripts are:
-
Modular – broken down into reusable components for common UI patterns
-
Readable – clean naming, consistent conventions, and clear purpose
-
Resilient – able to handle dynamic elements, async behavior, and minor UI changes
-
Self-validating – with built-in assertions for each key step
Using patterns like the Page Object Model (POM) can dramatically reduce script maintenance as your UI evolves. A stable test script foundation prevents flaky tests and makes scaling your automation effort much easier.
3. A Stable, Realistic Test Environment
Even the best scripts will fail if the environment is unstable. An effective test environment mirrors real-world conditions as closely as possible.
This includes:
-
Reliable hardware and browsers (physical or virtual)
-
Clean test data that reflects real user scenarios
-
Consistent app state between runs
-
CI/CD integration so tests run automatically with every code change
Cloud-based platforms like MuukTest can remove the burden of managing infrastructure by offering on-demand devices, browsers, and parallel test execution, all without maintaining your test lab.
When these components work together — the right tool, clean test logic, and a stable environment — your automated UI tests become fast, trustworthy, and scalable. For engineering teams under pressure to deliver quality at speed, building this foundation is the difference between test automation that slows you down and one that drives velocity.
Automated UI Testing Tools & Software
Choosing the right automated UI testing software is a crucial decision for successful automation implementation. The tools and frameworks you adopt will impact how easily your team can create, run, and maintain UI tests. Below are some of the most popular UI automation tools (open-source and free) and their characteristics:
| Tool | Best For | Strengths | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selenium | Web applications across multiple browsers; extensive flexibility. | Supports many languages (Java, Python, C#, JavaScript) and all major browsers. A huge community and ecosystem of plugins and extensions. Can automate complex scenarios and integrates with many other tools. | Steeper learning curve. Requires more coding and custom framework setup, which can lengthen initial implementation time. Test script maintenance can be effort-intensive without good practices. |
| Cypress | Modern web apps (especially single-page applications); teams with strong JavaScript/TypeScript skills. | Developer-friendly and easy to get started. Runs tests directly in the browser for fast feedback with automatic reloads and powerful debugging. Especially great for front-end developers since tests are written in JavaScript. | Officially supports primarily Chromium-based browsers (though expanding to others). Not ideal for scenarios requiring multiple browser tabs or cross-domain interactions. Geared mainly towards testing web UIs (less suited for non-web UI or native app testing). |
| Playwright | Cross-browser web testing with a modern API; teams using JavaScript/TypeScript, Python, or other supported languages. | Comprehensive cross-browser support out-of-the-box (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit). Supports multiple languages and has features like auto-waiting and headless execution, which make tests more reliable and easier to write. Good for testing modern web apps with a single framework for all browsers. | Introduced relatively recently in 2020, it has a smaller community than Selenium. Documentation and community resources, while growing, are not as extensive as Selenium’s yet. Some developers need to get used to its async programming model (especially in Node.js). |
| Appium | Mobile app testing (iOS and Android, native or hybrid apps); teams that need to automate mobile UI. | Can automate real mobile devices, emulators, or simulators. Uses a WebDriver protocol similar to Selenium, and supports multiple languages for writing tests. Enables the reuse of automation skills for mobile testing. | Setup and configuration can be complex, involving tasks such as dealing with mobile device drivers and OS-specific settings. Test execution is slower compared to web UI tests, due to the overhead of launching apps and interacting with mobile UIs. Debugging failures on mobile can also be more involved. |
In addition to these widely used frameworks, many teams are turning to no-code/low-code and AI-powered solutions to simplify and scale UI automation. These approaches often provide user-friendly interfaces or recorders to build tests without heavy scripting, and in some cases, use AI to adapt to UI changes and reduce test maintenance.
For example, MuukTest is a test automation solution that helps teams accelerate UI test automation without needing to build frameworks or manage maintenance in-house. Our QA experts partner directly with engineering teams to deliver reliable, high-coverage UI test suites tailored to your product and stack. Under the hood, we leverage robust tools like Selenium or Playwright, but we handle the complexity so your team can focus on shipping with confidence.
This type of expert-led service is especially valuable for organizations with limited in-house automation bandwidth or teams that want to fast-track test coverage without hiring or upskilling internally.
Tip: When evaluating automation options, consider not only the tools themselves but also the support structure. The best choice is one your team can implement and maintain—whether that’s a self-managed framework, a hybrid approach, or a trusted partner like MuukTest.
Best Practices for Implementing Automated UI Testing
Getting started with UI test automation can feel daunting, but following a few key best practices will set you up for success. These guidelines will help you maximize the benefits of automation while avoiding common pitfalls:
Select the Right Test Cases
Not every test should be automated, focus on high-impact, repetitive, and tedious test cases first. Ideal candidates for automation are scenarios that need to be run frequently (e.g., regression tests for each release) or tests that involve many steps and data combinations that would be tedious to perform manually.
Think of the tasks your team repeatedly executes, such as filling out the same forms or running through the same checkout process each sprint – those are prime targets for automation scripts. By prioritizing these, you get the highest return on investment: the automation effort frees up a significant chunk of time and catches regression bugs early. Conversely, avoid automating one-off tests or highly complex scenarios that rarely occur – those are better left for manual exploratory testing.
In short, be strategic about what to automate. Start with tests that cover core user journeys and critical functionalities that must always work, such as login, account creation, and transactions, and expand from there. This ensures your automation suite delivers value quickly and doesn’t become a maintenance burden for little benefit.
Maintain High-Quality Test Data
Reliable test data is the foundation of reliable tests. If your automated tests use inconsistent or unrealistic data, you may get false failures or passes, confusing the results.
Treat test data setup as a first-class part of your automation strategy. This could mean seeding a test database with known records before tests run, using factory scripts to create fresh data (e.g. new user accounts) as needed, or employing data generation tools. Ensure your tests clean up data when appropriate (to remain idempotent) or have access to a reset state. For example, if you’re testing an “edit profile” workflow, ensure the user data you start with is in a known state (perhaps create a new user via API at the start of the test) so the test outcome is predictable.
Poor test data management can lead to flaky tests. For example, a test might fail only because the user it was expected to edit did not exist. By investing time in setting up and tearing down test data, you ensure that your automated UI tests run in a controlled, known environment. The result is more accurate results you can trust.
Ensure Test Independence
Each automated UI test should be self-contained and independent of others. This means tests can run in any order, and the outcome of one test doesn’t affect the next test.
Dependence between tests often causes a domino effect; if one test fails (say it didn’t clean up a logged-in session), subsequent tests might fail not due to bugs in the app, but due to that residual state. To avoid this, design tests to set up their preconditions and clean up after themselves. For instance, if Test A creates a new record, Test A should delete it (or use a separate test database that’s wiped between runs).
Independence makes it much easier to pinpoint failures. You know a failing test is due to an issue in that specific functionality, not a side effect from earlier tests. It also allows you to run tests in parallel, as they won’t interfere with each other’s data or state, which significantly speeds up execution in continuous integration (CI) pipelines. Adopting practices like starting each UI test from a fresh app state (e.g., launching the browser anew, not relying on prior login state unless explicitly part of the test) will help.
Implement Consistent Naming and Structure
Treat your test code with the same care as application code. Using clear, consistent naming conventions for your test cases, data files, and page object classes (if using the Page Object Model) is essential for long-term maintainability. When every test’s purpose is obvious from its name (e.g., Checkout_With_Invalid_CreditCard_Shows_Error), your team can quickly understand and trust the suite.
Consistent naming and organization also help when you have dozens or hundreds of tests – it’s easier to find, update, or review tests when they follow a predictable structure. Establish a standard for naming tests and structuring test suites, such as grouping them by feature or user persona. Additionally, if you’re using a framework that supports the Page Object Model (POM) pattern, take advantage of it. POM encourages separating the details of the UI (locators and interactions for a given page or component) into dedicated classes, which your tests then use. If the UI changes, you update the locator in one place (the page object) rather than in every test. It’s a form of abstraction that significantly reduces maintenance effort when the application evolves. Overall, well-structured tests (with good naming and possibly a layered architecture, such as a POM) will be easier for anyone on the team to read, run, and update as needed.
Integrate with CI/CD Pipelines
To truly reap the benefits of automated UI tests, integrate them into your Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline. Rather than running tests ad-hoc, you want them to execute automatically on every code change or build. For example, you might configure your CI system (such as Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions) to run the UI test suite whenever a developer merges new code or at least once daily. This integration provides a safety net – if a code change inadvertently breaks a key UI flow, the automated tests will catch it immediately and alert the team. In an Agile development environment, this rapid feedback is crucial to prevent regressions from reaching production. Ensure that you allocate sufficient infrastructure for these test runs. You can use cloud-based testing services or containers to spin up browsers for testing. Also, failures in CI test runs should be treated as stopper issues that need attention. This creates a culture of quality where code isn't considered “done” until it passes the automated checks. By embedding UI tests into CI/CD, you effectively have a continuous quality guardrail: every new feature or bug fix is automatically validated against your app’s core user journeys. This practice gives engineering leaders peace of mind that accelerating delivery won’t mean sacrificing the user experience.
Overcoming Common UI Test Automation Challenges
Automated UI testing brings tremendous benefits, but it also has its challenges. Being aware of these potential hurdles and how to address them will help ensure your automation initiative succeeds. Here are some common challenges teams face with UI test automation and strategies to overcome them:
Handle Dynamic Elements and Flakiness
One of the most frequent headaches is flaky tests – tests that sometimes pass and sometimes fail, even though the code hasn’t changed.
Flakiness often stems from the dynamic nature of modern UIs. Elements may take time to load, animations may delay a button from becoming clickable, or content may update asynchronously. If a test script tries to click or assert something before the UI is ready, it will fail even though the application is actually fine. The solution is to build in robust synchronization (wait) strategies. Ensure your tests wait for elements to appear or become interactable before proceeding.
Most frameworks offer explicit waits (waiting for a specific condition like “element X is visible”) and implicit waits (a default short pause for all element finds). Use them wisely: for example, after navigating to a dashboard page, wait for the key table or text to load before verifying it. Additionally, use reliable locators for elements – dynamic IDs or changing XPaths can cause tests to break; prefer stable identifiers like static IDs or data attributes. By making your tests a bit more patient and intelligent about timing, you can eliminate a large portion of flaky failures. In summary, flakiness is often a test issue, not a product issue. Address it by refining your scripts to handle the dynamic nature of the UI (such as waiting for AJAX calls to finish, etc.); you’ll have a much more reliable suite.
Manage Cross-Browser Compatibility
Ensuring your web application works across all browsers and devices is a classic challenge, and this also applies to your automated tests.
You want your UI tests to run on Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and so on, to catch any browser-specific issues, such as CSS that breaks on Safari, for example. Doing this manually is extremely time-consuming, but automation can help by running the same test scripts on different browsers. However, setting up a cross-browser testing environment can be tricky. You might need a grid of browsers (using tools like Selenium Grid, BrowserStack, or others) to run tests in parallel. Investing in a reliable infrastructure or service for cross-browser testing is essential.
Cloud-based testing services can provide up-to-date browsers and devices on demand, which is often easier than maintaining a virtual machine (VM) zoo yourself. Also, design your tests to be browser-agnostic; the scripts should not rely on browser-specific behavior.
If your automation tool or framework has quirks on specific browsers, account for them or configure the tests to handle the differences. Cross-browser testing will significantly increase your test coverage, but be sure to monitor test execution times – running every test on every browser can slow down the pipeline. Many teams solve this by running a core smoke test suite on all browsers frequently and the full regression suite on a primary browser, along with a daily full cross-browser run. By planning your approach and using the right tools, you can confidently deliver a consistent UI experience on all platforms without multiplying manual effort.
Adapt to Rapid UI Changes
User interfaces are living, breathing parts of software; they change often due to new features, redesigns, or improvements. A big challenge in UI test automation is maintaining tests in the face of UI changes. A locator that worked yesterday might not work after updating the UI today. The best way to combat this is to make your tests as maintainable as possible and anticipate change. Using the aforementioned Page Object Model is one technique – encapsulating the knowledge of the UI structure in one place. So, when the UI changes, you update the page object, and all tests using it are updated simultaneously.
Another strategy is to use more robust selectors for elements – for example, many teams add special attributes like data-test-id in their HTML, specifically for automation to latch onto, which are less likely to be altered by designers.
Prioritize automating stable flows: if a section of the app is undergoing constant UI changes, it may be wise to hold off on automation until it stabilizes and focus on relatively stable parts of the app. Additionally, involve your development team in knowing that tests exist. If developers are aware of an automated test for a feature, they can notify QA of impending changes or even update the test locators as part of their change. Developers might even update the page object in a truly collaborative culture.
Regularly reviewing failing tests is also key. When a group of UI tests suddenly fails, it’s often an indicator of a deliberate UI change—treat that as part of the deployment process to update the tests. By designing for maintainability and fostering dev-QA collaboration, you can keep your automated test suite in sync with evolving UI without excessive effort.
Balance Automated and Manual Testing
It’s essential to remember that automated testing does not entirely replace manual testing. Some aspects of quality are best evaluated by humans, such as usability, exploratory testing of new features, look-and-feel nuances, or one-off scenarios. A common mistake is trying to automate “everything” and then discovering that the automated tests are brittle or not effectively covering the real user perspective.
The key is to find the right balance. Use automated UI tests to cover regression scenarios and repetitive checks, things you have to run often, and that have expected outcomes that can be programmatically verified. This frees up your human testers to do what they’re great at: exploratory testing, uncovering edge cases through creative use, and doing usability testing that a script could never do.
In practice, after you automate a test suite, continue to have QA engineers (or developers) perform exploratory test sessions for each major feature. The automated tests will catch known issues. In contrast, the human tests might reveal unknown issues or UX improvements. Also, for any bug found manually, consider adding an automated test if it’s something that could regress. By combining forces, you ensure broad coverage through automation and gain deep insights through manual testing. As an engineering leader, encouraging this mixed approach will lead to higher quality than either approach alone.
Address Team Skill Gaps
Implementing automated UI testing requires specific technical skills, including knowledge of programming, familiarity with test frameworks, an understanding of web technologies (such as HTML, CSS, and DOM), and even DevOps skills for integration into Continuous Integration (CI). If your team is new to automation, there can be a learning curve. It’s crucial to invest in training and upskilling your team members. Start with one or two pilot projects where the team can learn by doing, perhaps with mentorship from someone experienced.
Encourage developers and QA to work together on automation; this cross-pollination can accelerate learning. Additionally, choose tools that match your team’s skill level. For instance, if your QA team is very comfortable with JavaScript, a tool like Cypress or Playwright (which uses JavaScript or TypeScript) might be easier to adopt than something like Selenium with Java. There are also many community resources, courses, and tutorials available for popular tools. Allocating time for your team to go through these will pay off in faster test creation later.
Another option is to bring in external expertise to jumpstart your automation. This could mean hiring a test automation engineer or partnering with a company that specializes in test automation. For example, you might engage a service like MuukTest to get expert QA architects working with your team. They can help set up the initial framework, write a suite of stable tests, and mentor your team on best practices. This kind of partnership can help you accelerate your progress and quickly overcome skill gaps. Over time, as your team gains proficiency, they can take over and continue expanding the test suite.
Your goal as a leader is to ensure the team has the necessary skills and support to make automation sustainable. With proper training, the right tool choice, and possibly a boost from experts, even a team new to automation can successfully implement and maintain a robust automated UI testing program.
Conclusion
Automated UI testing is more than a technical enhancement; it’s a strategic enabler for faster, higher-quality software delivery. By offloading repetitive checks to reliable scripts, you empower your team to focus on innovation without fearing that new changes will break the user experience. A well-designed UI test suite acts like a safety net, catching issues in hours that might otherwise take weeks, or an angry customer email, to discover.
We’ve explored how UI automation testing improves efficiency, accuracy, and confidence, especially when combined thoughtfully with API testing and solid best practices. Yes, there are challenges on the journey – flaky tests, evolving UIs, and the need for new skills – but these can be overcome with the right approaches and tools in place.
The payoff for overcoming these challenges is substantial: faster release cycles, happier users, and a competitive edge in quality. Instead of being a bottleneck, your QA process becomes a catalyst for agility. Teams that master automated UI testing deliver updates with greater confidence and consistency, which ultimately drives business success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between automated UI testing and manual UI testing?
Manual testing involves a human tester interacting with the application's interface, clicking buttons, filling out forms, and checking for issues. Automated UI testing uses scripts to perform these same actions automatically. This automation saves time and resources, especially for repetitive tests. Manual testing is still valuable for tasks requiring human judgment, like evaluating usability.
How do I choose the right automated UI testing tool?
The best tool depends on several factors, including the type of application you're testing (web, mobile, desktop), the programming languages your team uses, and your budget. If your team primarily uses JavaScript, Cypress might be a good fit. Appium is a popular choice for mobile app testing. Selenium is a versatile option for web testing that supports multiple languages. Research different tools and consider your team's skills and project requirements.
What are some common challenges in automated UI testing, and how can I overcome them?
Dynamic content and timing issues can lead to flaky tests. Use explicit waits to ensure elements are loaded before interacting with them. Cross-browser compatibility can be tricky; use cross-browser testing platforms or cloud-based solutions. UI changes require updating tests; use a page object model (POM) to make updates easier. Finally, ensure your team has the necessary skills or consider partnering with a company like MuukTest for expert support.
How can I integrate automated UI testing into my Agile workflow?
Integrate your automated tests into your CI/CD pipeline to run tests with every code change. Encourage collaboration between developers and QA to create robust tests. Consider a test-driven development (TDD) approach, where you write tests before writing code. Design tests that can adapt to frequent UI changes by using robust locators.
How do I measure the success of my automated UI testing efforts?
Track key metrics like test execution time, test coverage, defect detection rate, and test pass/fail rate. Analyze test results to identify trends and areas for improvement. Monitor the time spent on test maintenance to optimize your tests for efficiency. Regularly review and update your tests to ensure they remain effective and aligned with your application's evolution.