What Is AI-Generated Code?
AI-generated code is software code written partially or entirely by artificial intelligence systems, typically large language models (LLMs). Developers provide prompts or instructions, and the AI generates functions, scripts, tests, or full modules based on learned patterns rather than true understanding, which can introduce variability and hidden logic risks.
- AI-generated code is probabilistic, not intentional. It predicts patterns based on training data, which means syntactically correct code can still contain hidden logic flaws.
- Unpredictability is the new risk category. The same prompt can produce different outputs, making consistency and edge-case testing more critical than ever.
- QA must evolve from validation to interpretation. Testing AI-generated code requires verifying business intent, assumptions, and real-world behavior, rather than just ensuring the code runs.
- Development velocity shifts the bottleneck to QA. As AI accelerates coding, scalable regression testing and risk-based prioritization become essential.
- Human judgment remains irreplaceable. Generative AI can create code, but it cannot understand user context, business impact, or consequences of failure.
AI isn’t just assisting software teams anymore; it's creating software. From auto-generated functions to entire modules scaffolded by large language models, generative AI has officially entered the developer’s toolkit. But as more code is written by machines, a new reality emerges: the role of QA is becoming more critical, more creative, and more strategic than ever before.
For years, QA engineers ensured that human-crafted code met standards of correctness and quality. But what happens when the code comes from a model that doesn’t “think,” doesn’t “understand,” and sometimes doesn’t even follow its own patterns?
Before we proceed into the blog, consider a few questions worth thinking:
- If AI can generate 20 versions of the same function, which one is the right one?
- How do you test logic that didn’t pass through a developer’s intuition?
- What happens when AI-generated code looks perfect on the surface, but fails in the edge cases?
- Are your current QA practices ready for a world where code is built at machine speed?
These are the challenges facing today’s QA engineers, and they require a more structured, scalable approach to quality strategy. Let’s explore how testing should evolve when meeting AI-driven development.
How Generative AI Is Changing Software Development
In traditional development cycles, humans wrote code line by line. They built logic intentionally, often leaving behind clues, comments, naming conventions, and structures that made the thinking traceable.
Generative AI breaks this pattern. Tools like GitHub Copilot, ChatGPT, CodeWhisperer, and specialised LLMs can:
- Generate functions from a single sentence
- Propose architectural patterns
- Suggest refactors, tests, and design alternatives
- Produce hundreds of lines of code in under a minute
This acceleration creates pressure on QA processes that were never designed for such speed.
So ask yourself: Are you prepared for testing in a world where development is no longer the bottleneck?
Adapting QA for AI-Driven Development
As generative AI accelerates development cycles, QA must evolve from reactive, manual validation to a structured, scalable system embedded directly into the delivery pipeline. The shift typically follows a clear progression:
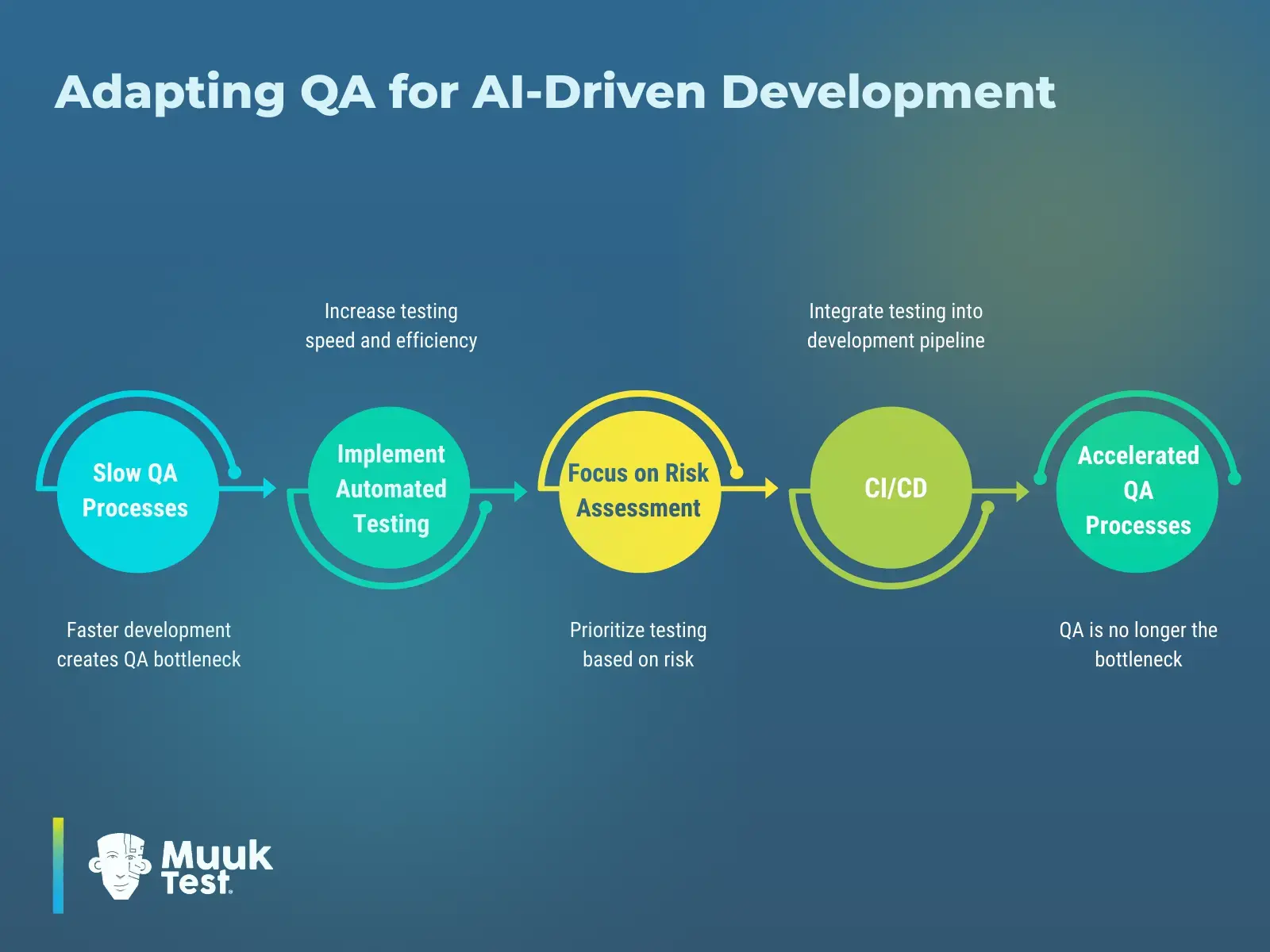
Faster development often exposes QA as the bottleneck. By introducing automated testing, prioritizing test coverage based on risk, and integrating validation into CI/CD pipelines, teams transform QA into a continuous, scalable function. Ensuring quality keeps pace with development instead of slowing it down.
What Are the Risks of AI-Generated Code?
AI introduces a unique category of risk: unpredictability. Developers may type the same prompt twice and receive two different code solutions. Sometimes one version is brilliant, while the other contains subtle logic errors that only surface under rare conditions.
Generative AI may also:
- Hallucinate non-existent APIs
- Invent variables that don’t exist
- Handle edge cases inconsistently
- Produce code that is syntactically correct but semantically wrong
- Misinterpret vague requirements
- Introduce security vulnerabilities unintentionally
A human developer makes errors due to a misunderstanding of the problem. AI makes errors because it doesn’t understand problems at all. This difference forces QA to adopt new strategies grounded in validation, interpretation, and careful oversight.
The goal is to "Shift Left," meaning quality shouldn’t wait until the end of the sprint. It starts during feature planning. When the team discusses risks, test scenarios, and acceptance criteria upfront, this way, quality becomes everyone’s responsibility.
How Do You Test AI-Generated Code?
Testing predictable code is already challenging. Testing probabilistic code, where outputs may vary depending on prompts, context, or training data, pushes QA into new territory.
Quality engineers must now consider questions like:
- Does the generated code actually reflect the intended business logic?
- Are there hidden branches introduced by pattern-based generation?
Should the same prompt be tested multiple times to detect inconsistencies?
Does the code behave the same way with slight changes in input or environment?
Testing AI-generated code requires structured validation across multiple dimensions:
.webp)
To effectively test AI-generated code, QA teams should:
- Run multiple test executions to detect inconsistencies
- Validate stability under varying inputs and environments
- Identify hidden branches introduced by probabilistic logic
- Confirm alignment with business requirements
This multi-layered approach ensures AI-assisted development remains reliable, predictable, and aligned with real-world use cases.
Because outputs can vary, QA must design structured tests that validate consistency, edge-case handling, and logical integrity - not just surface-level functionality.
In many organisations, scaling QA frameworks to keep pace with AI-assisted development requires additional structure and oversight. Managed QA partners like MuukTest help teams strengthen regression coverage, expand edge-case testing, and adapt automation strategies as development velocity increases.
How a Managed QA Partner Can Help
As development accelerates with generative AI, QA must scale without becoming the bottleneck.
MuukTest works alongside engineering teams as a managed QA partner, combining AI-driven test automation with experienced QA experts who own the testing lifecycle end-to-end.
In AI-assisted development environments, this means:
- Designing risk-based test strategies around critical user flows
- Expanding regression coverage as code volume increases
- Identifying edge cases that AI-generated logic may overlook
- Continuously maintaining and stabilizing automated test suites
- Integrating testing directly into CI/CD pipelines
AI can generate code quickly. But it doesn’t validate business context, edge-case behavior, or real-world usage patterns.
That’s where structured QA ownership becomes essential, ensuring testing remains thoughtful, scalable, and aligned with real user impact.
Generative AI makes building faster. Quality systems must evolve just as quickly.
Common Challenges in Testing AI-Generated Code
-
New categories of defects unique to generative systems
-
“Invisible bugs” created by oversights in the training data
-
Increased security vulnerabilities
-
False trust in AI-produced output
-
Reduced explainability of logic
-
Harder-to-maintain code bases
-
Compliance gaps
Opportunities for QA in Generative AI Development
-
Rapid prototyping
-
More time for deep testing and analysis
-
Ability to automate low-level tests
-
Higher coverage and increased consistency
-
Faster iteration cycles
-
Automated documentation and refactoring
Whether your team experiences more risks or more opportunities depends on how effectively you adapt your QA processes and whether you have the right partner to guide that evolution.
For teams navigating AI-assisted development, having structured QA ownership becomes even more critical.
The Future of QA in the Age of Generative AI
As generative systems produce code at machine speed, QA becomes the function that ensures alignment between output and reality. It validates not just whether code runs, but whether it reflects business logic, protects users, and holds up under real-world conditions.
Quality professionals are no longer validating lines of code. They are validating assumptions, edge cases, and consequences.
-
As automation expands, QA safeguards context.
-
As AI accelerates, QA preserves standards.
-
As development speeds up, QA protects trust.
Food for thought:
-
Are you prepared to test logic generated by models instead of humans?
-
Does your organisation have a plan for managing generative unpredictability?
-
Is your QA strategy evolving as quickly as your development process?
-
Could partnering with a managed QA team strengthen your quality approach in this new era?
The future belongs to the teams that embrace AI thoughtfully and cautiously. With the right testing mindset and partners.
Generative AI does not eliminate quality assurance. It makes it indispensable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is AI-generated code?
AI-generated code is software created partially or entirely by artificial intelligence systems, typically large language models (LLMs). Developers provide prompts, and the AI generates functions, scripts, or full modules based on learned patterns rather than true understanding, which can introduce variability and hidden logic risks.
Why is testing AI-generated code different from traditional testing?
Testing AI-generated code is different because the logic is probabilistic rather than intentionally designed by a developer. The same prompt can produce different outputs, increasing the need for repeatability testing, consistency validation, and deeper verification of business logic.
What are the main risks of AI-generated code?
The main risks of AI-generated code include unpredictability, hallucinated APIs, hidden execution branches, inconsistent edge-case handling, security vulnerabilities, and reduced explainability. Even syntactically correct code can fail under real-world conditions.
How do you test AI-generated code effectively?
To test AI-generated code effectively, QA teams should run multiple test executions, validate stability under varying inputs, identify hidden logic paths, and confirm alignment with business requirements. Structured regression testing and risk-based prioritization help manage output variability.
Can AI-generated code be trusted without human QA?
No. AI-generated code cannot be trusted without human QA oversight. While AI accelerates development, it does not understand user context, compliance requirements, or long-term maintainability. Human judgment remains essential for validating assumptions and preventing hidden defects.
How should QA evolve for AI-driven development?
QA should evolve from manual validation to automated, risk-based, and continuously integrated testing. As development velocity increases, teams must shift left, expand regression coverage, and embed testing directly into CI/CD pipelines to prevent quality from becoming the bottleneck.









.png)